Installing PHP on Linux CentOS 7
To install PHP 7, you have to install and enable EPEL and Remi repositories on your CentOS 7
EPEL & REMI
EPEL ( Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux ) and REMI are just two between several useful yum repositories for RHEL (Red Hat Enterprise Linux) based systems.
- EPEL
- REMI
- RPMFusin
- ELRepo
- Webtatic
We need they to keep our systems up to date with latest packages, because these repositories having most of the RPMs required for our servers.
These repositories are created, maintained, and managed by Linux’s professional programmers, just as an example, the following GitHub link belongs to the creator or REMI repository:
Some packages are included in the repositories that are configured when the operating system is installed.
How to install EPEL
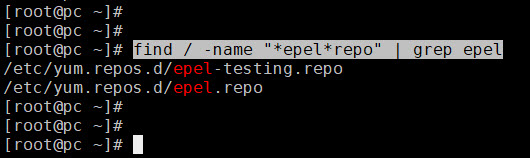
yum install https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/epel-release-latest-7.noarch.rpmHow to find EPEL files
find / -name "epel*repo"How to install REMI
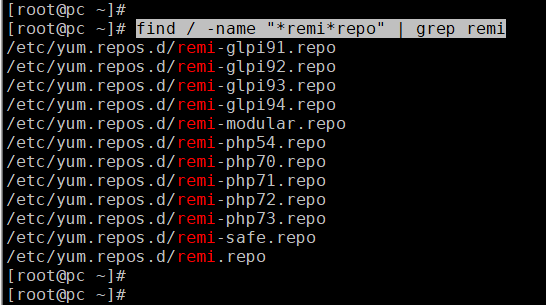
yum install http://rpms.remirepo.net/enterprise/remi-release-7.rpmHow to find REMI files
find / -name "remi*repo"YUM
YUM ( Yellowdog Updater, Modified ) is a command-line package management utility for RPM-based Linux systems.
Yum is useful for RPMs which have dependencies, Yum searches for all dependencies of any RPM in all available repositories.
YUM Utils
Yum Utils is a collection of useful programs for managing yum repositories and packages. Its main purpose is to extend yum’s default features.
Sysadmins often use It for managing (enabling or disabling) yum repositories as well as packages without having to do any manual configuration.
How to install Yum-config-manager
yum install yum-utilsOne of the programs provided by yum-utils is yum-config-manager, which you can use to enable Remi repository as the default repository for installing different PHP versions.
How to use Yum-config-manager
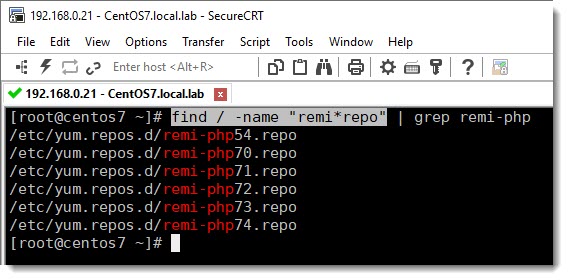
We already saw with the command “find” that our system has several PHP versions inside the REMI folder, we can then choose one of them and enable it using the yum-config-manager, as shown below:
yum-config-manager --enable remi-php73Basically, whatever is inside REMI can be enabled using the above command, see below image, you already have multiple versions of PHP ready to be enabled.
Installing PHP along with its modules
yum install php php-mcrypt php-cli php-gd php-curl php-mysql php-ldap php-zip php-fileinfo PHP version
php -v[root@centos7 ~]# php -v
PHP 7.3.15 (cli) (built: Feb 18 2020 09:25:23) ( NTS )
Copyright (c) 1997-2018 The PHP Group
Zend Engine v3.3.15, Copyright (c) 1998-2018 Zend Technologies
[root@centos7 ~]# This procedure can be followed either for installing PHP for the first time and also to upgrade PHP to a newer version.
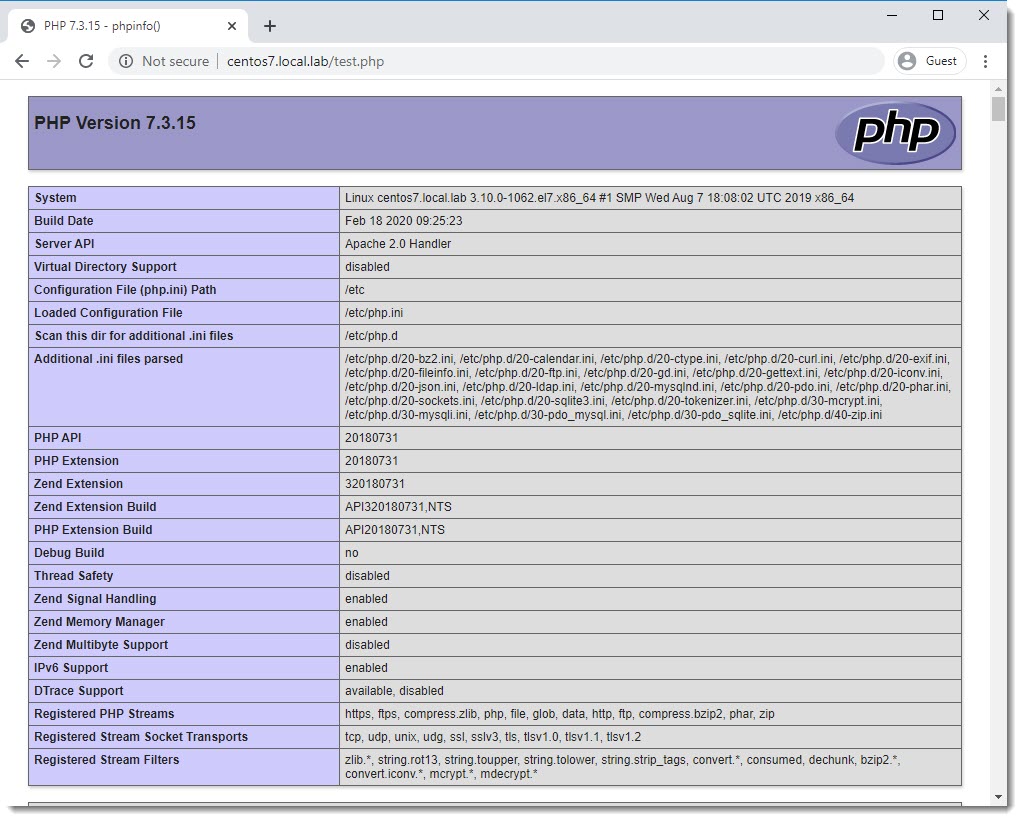
Test PHP using the phpinfo() function
The phpinfo() function is a built-in function that can be used to show configuration details, installed modules, etc.
<?php
phpinfo();
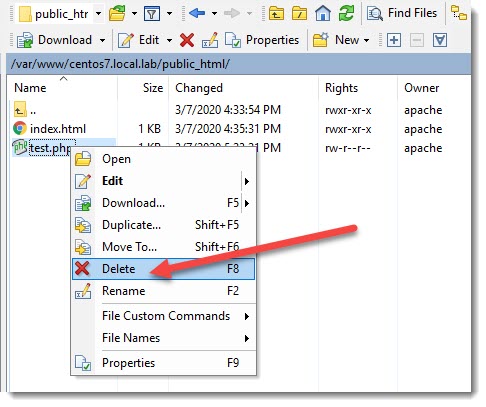
?>You can create a simple file including this function and delete it immediately after you saw all the PHP information displayed via html page.
http://centos7.local.lab/test.phpIn case the page is not loaded you can try reloading Apache.
systemctl restart httpd.serviceCheck Apache status after the reset
systemctl status httpd.serviceDelete the test file
Do not forget to delete the test file because it might give a hacker information they need to attack the server.